The IT industry loves a new paradigm. It provides the opportunity to discuss innovative technology while introducing a whole range of existing products and services in totally new ways. The latest paradigm is Edge Computing. Analysts describe Edge as the way to move data processing nearer the business, connecting millions of IoT devices, placing containers of equipment in fields all enabled with the speed of 5G networks.
This high-level description ignores the fact that highly-distributed computing has been around for decades. Edge is just a lot more distributed, more mission critical, more connected and smarter.
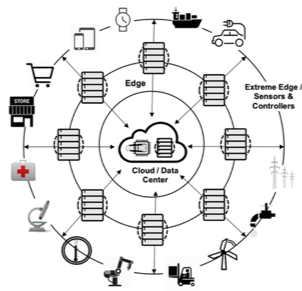
No matter how intelligent the end-point all Edge approaches share the same architecture. Core data center(s) with satellite locations that store and process data and interact with end-points – intelligent and passive. This architecture may be overly simplistic as there can be more layers and the extreme edge (the ultimate end-point) may be a matrix of devices aware of each other.
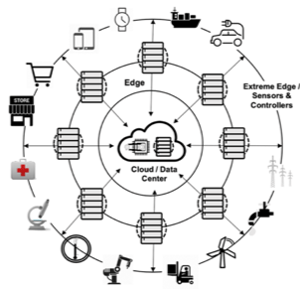 There is no standard Edge definition. There is no standard Edge environment. Edge is defined by each business and enabled by application architecture. It consists of network gateways, data centers and all things IoT.
There is no standard Edge definition. There is no standard Edge environment. Edge is defined by each business and enabled by application architecture. It consists of network gateways, data centers and all things IoT.
Edge Delivers
- Data-stream acceleration, including real-time data processing without latency.
- Smart applications and devices respond to data immediately with no lag.
- Processing of large amounts of data near the source.
- Reduced internet bandwidth usage eliminating cost.
- Data processing without placing it into a public cloud.
- Improved customer experiences.
No matter the Edge objective there are common attributes.
- The Edge delivers distributed application services, provides intelligence to the end-point, accelerates performance from the core and collects and forwards data from the Edge end-point sensors and controllers.
- Edge can be the size of sensors and controllers, a small number of network/server racks, a container full of equipment or a large air-conditioned data center.
- Edge locations are ‘lights out’, with no local skills or support requiring the use of technology that is highly resilient/fault tolerant to provide remote monitoring and control.
- Edge locations are highly distributed with highly diverse equipment requiring the use of technology that can scale, monitor and manager heterogeneous environments seamlessly with minimal effort.
- Edge environments demand a high-level of physical, network, systems and data security.
- Edge locations require the ability to track and guide physical change, support and maintenance.
For companies that have an established highly distributed IT environment, with consumers using mobile tech, Edge may be considered an evolution rather than a revolution. However, Edge computing takes distributed IT mainstream and to new levels of complexity. It introduces challenges requiring solutions specifically focused on delivering capabilities without the customization, disparate control, monitoring or cost required using products originally developed for use in a traditional data center or cloud.
RF Code for Edge environmental and asset tracking products have been developed specifically for enterprises requiring a solution that removes the complexities of managing the Edge. It delivers a massively scalable, trusted source that seamlessly integrates, visualizes, reports and alerts all key Edge location activities to ensure there are no surprises ensuring uninterrupted business availability.

Learn about The Edge: what it is, where it is, its much-vaunted benefits, and the obstacles and hazards IT professionals need to address to ensure their edge deployments deliver the rewards their businesses demand. Download our white paper "Standing at the Edge? Look Before You Leap" today.