This is the first in a four-part weekly series that examines RF Code's Edge Computing model. The goal of this series is to provide a foundational understanding of the core Edge requirements, the Edge objective values, product relevance and positioning, and how companies can evaluate and assess their path to Edge.
Introduction
Edge computing changes how IT services are delivered, and this has changed how products are chosen, delivered and used. Edge computing demands management products are evaluated on more than features and functions.
The impact of Edge is transformational. It requires IT organizations to evaluate how they are organized, the changes in process, the relevance of existing technology and most importantly, the ability to deliver business value. The immediate challenge for Edge Computing is it is diverse, confusing and undefined. Describing it in high-level abstract or generic terms is worthless as it provides little clarity and promotes vendor ‘edge washing’ where all products can be creatively positioned to address Edge.
Leveraging customer, analyst and partner information RF Code has developed this Edge model.
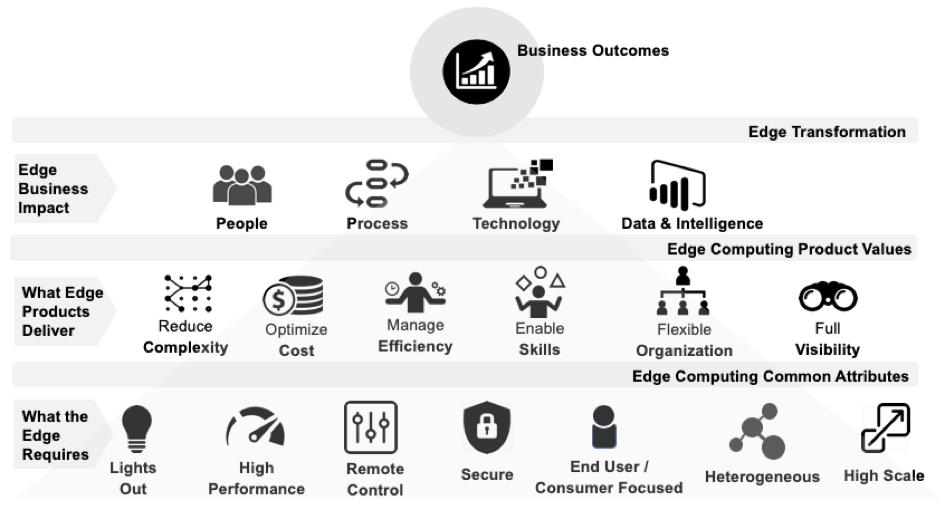
Figure 1. The Edge Model
In this first entry in our four-part series we will look at the first layer in this mode, "What the Edge Requires." By this, we mean the attributes of an Edge deployment that differentiate it from traditional data centers.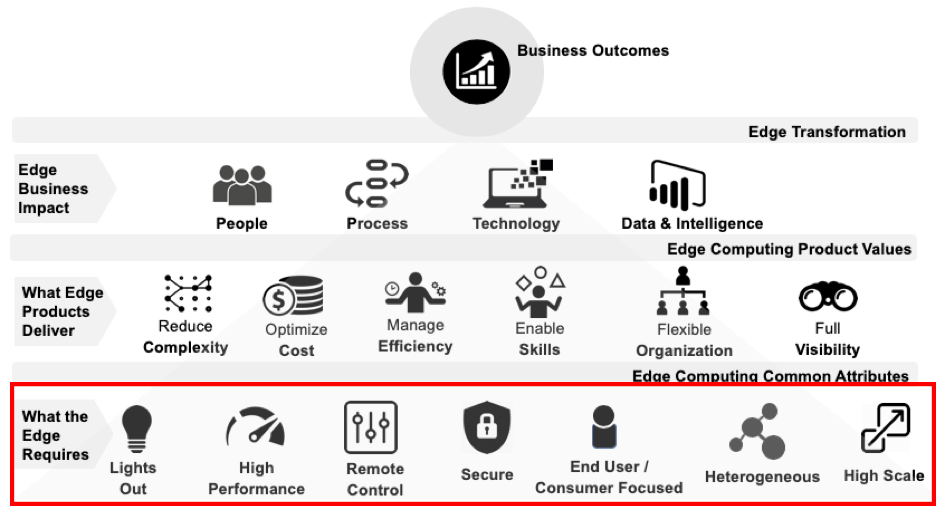
Edge Computing Classification
Edge computing moves data processing nearer business operations. It has many variations, with many IT professionals regarding it as an evolution of the distributed ‘lights out’ data center concept. No matter how intelligent the end-point all Edge approaches share the same architecture. Core data center(s) with satellite locations that store and process data and interact with end-points.
Edge consists of network gateways, data centers and all things IoT. The purpose of the Edge is to deliver distributed application services, provide intelligence to the end-point, accelerate performance from the core data systems or collect and forward data from the Edge end-point sensors and controllers.
The absence of an agreed and accepted Edge computing definition demanded we create our own resulting in three different types of use-case:
- Remote ‘Lights Out’ Edge Data Centers can be a small equipment rack in multiple remote locations or multiple large data centers. It is the most diverse, non-standard Edge environment, requiring new organizational models, sophisticated software application architectures and a high level of abstraction to visualize, deliver low touch control and the ability to scale and manage a heterogenous, mix of equipment.
- Container IT Edges is where converged systems live. This environment consists of a solution stack comprising of one or more of the following; servers, OS, storage, network and optimized power and cooling to support all the equipment in the contained environment. The containers are highly standardized however, customization is available to suit specific Edge requirements with options for additional components.
- Internet of Things (IoT), where highly available processors enable real-time analytics for applications that can't wait to make decisions. IoT end-points continue to get smarter with greater ability to work independently and make decisions without regular communication with a core platform.
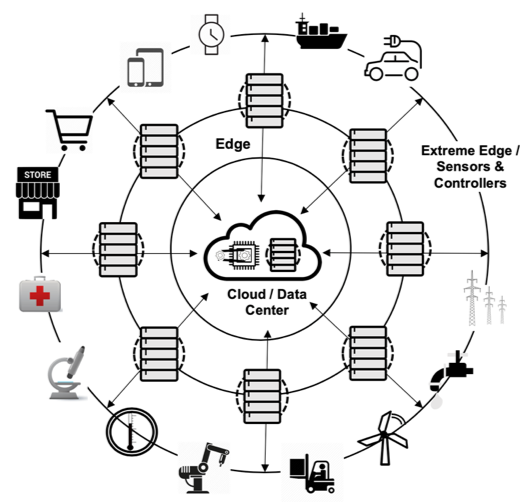
Figure 2: The Three Edge Use-Case Eco System
What the Edge Requires
An Edge environment exhibits attributes that differentiates it from other environments such as cloud or on-premise data centers. Products used to enable Edge must ensure that the attributes are met. The following are seven common attributes specific to use case 1 and 2 Edge computing environments.
Figure 3: The Seven Common Edge Attributes
Each attribute area contains values that fulfill the attribute. The values are needed to meet the attributes. The following is a list of the Edge common attributes, the values and supporting value details.
Lights Out
- Locations function without local human resources
- IT skills and resources optimized
- IT personnel placed where the business needs them
- Edge locations added without requiring an increase in skills and resources
- Locations monitored and controlled remotely
- Edge managed and monitored using tools that do not require local support
- Edge facilities monitored and managed as an holistic environment
- Change at the Edge managed, monitored and guided remotely
- Edge environment and infrastructure monitored in real-time, no blind spots
- Infrastructure and environment monitored in-line with Edge service delivery
- Physical access and local activity monitored
- Software, hardware and environment monitoring unified to show overall Edge status
High Performance
- High performing data communication to/from the highly distributed Edge environment
- Edge environment and infrastructure performance monitored to support the end-to-end IT service delivery metrics
- Environmental conditions at the Edge aligned with the impact on IT services
- Edge performance evaluated against SLA’s and cross Edge facility comparisons
- Edge equipment fully supported without requiring customization
- Service performance efficiencies delivered through the elimination of custom work
- Personnel performance increased through the elimination of manual activity and the unification of monitored data
- Environment performance delivered by unifying disparate conditions and automatically evaluating the impact on the IT services delivered at the Edge
- High availability, no single point of failure
- Edge environment has high-availability and failover built in to mitigate the risk of failure
- Edge status information delivered even when outages to the infrastructure and environment occur
- Monitoring tools do not stop working when the Edge experiences network or power degradation
Remote Control
- Remote control and monitoring of IT assets and environmental systems
- Infrastructure, software and environmental systems controlled and monitored without requiring local personnel
- Edge infrastructure and environmental systems that do not have remote monitoring capabilities are monitored with solutions that can integrate with them
- Conditions requiring a human presence at the Edge facility are enabled through monitoring and supported with remote guidance
- Environmental conditions monitored with alerts created when exceptions are detected
- Conditions are consolidated to provide an overall environmental Edge state
- Environmental conditions are correlated to provide cause and impact data
- Environmental monitoring is integrated with service management solutions
- Asset movement and access to facility monitored and tracked
- Assets are tracked in in real-time to their physical (actual) location
- Network outages and power disruption should not prevent assets from being tracked
- Environmental conditions are associated with the impacted assets
Secure
- Connectivity to and within Edge secured in-line with industry and corporate policy
- Edge environment managed against change management policy and controls
- Physical changes at the Edge accomplished under remote supervision to reduce risk
- Change activity recorded and logged
- Edge management tools provide and enforce access permissions for different roles
- Edge tools must have roles-based access
- Edge monitoring dashboards customized around roles
- Monitoring and reporting data delivered with access controls and granular permissions
- Real-world view of physical access and subsequent activity at all Edge locations
- Controlled and monitored access to Edge locations
- Recorded video of Edge facility activity
- Alerts created when movement is detected
End User / Consumer Focused
- Consumer experience captured and used to measure Edge success
- Constant feedback on application availablity, performance and response times
- Issues managed in-line with SLA’s with feedback on responsiveness and impact
- Tools ensure business activity is factorered into real-time Edge status monitoring
- Edge managed and supported in-line with the business service levels
- Performance and availability managed in-line with service levels
- Environment and infrastructure relationships mapped to manage environmental impact on business assets
- Support priorities dynamically adjust inline with business activity
- Continual location comparisons enable efficiency and performance change and identify and eliminate issues and weaknesses
- Enterprise Edge performance evaluated to assess high and low performing locations
- Edge infrastructure and environmental system comparisons assessed to identify high and low performing vendor equipment
- Location capacity and consumption monitored to identify areas of improvement and optimization
Heterogeneous
- Edge managed consistently irrespective of technology type or vendor
- Holistic Enterprise Edge infrastructure and environmental conditions monitored
- Information normalized from multiple sources
- Edge state known with issues addressed using a single source of truth
- Out-of-the-box management support for all Edge systems
- Edge systems managed and monitored without customization
- Out of the box support for all new and updated Edge equipment
- No migration impact when changing Edge systems
- Elimination/abstraction of proprietary hardware monitoring
- Single source of truth across all infrastructure and environmental systems
- Monitoring data normalized and reported
- Elimination of multiple displays and dashboards
High Scale
- Management scales to hundreds or thousands of different size locations
- Edge environment scale managed without impact or an increase in complexity
- Edge environment scale managed without service degradation
- Maps and dashboards allow scale to be accomplished without impacting visualization and an ease of understanding
- Locations added and removed without impacting business
- Change accomplished without an impact on IT services
- Management abstraction allows freedom of choice for Edge systems
- New Edge systems and locations added with low cost, low impact and no additional skills
- Performance delivered consistently across all locations
- Performance of Edge monitoring unaffected by growth within Edge locations
- Performance of Edge monitoring unaffected by growth of Edge locations
- Monitoring performance not impacted by Edge systems diversity
RF Code for Edge is designed to meet the requirements of the Edge with functionality that delivers the common Edge attributes.
|
Common Edge Attribute |
RF Code CenterScape for Edge |
|
Lights Out • Locations function without local human resources • Locations monitored and controlled remotely • Edge environment and infrastructure monitored in real-time, no blind spots
|
• Single, trusted view of all Edge locations from remote monitors • Wireless environmental health monitoring and asset tracking negating reliance on the network • Remote guided maintenance and support for personnel required to visit the Edge facility • Live video of the Edge facility triggered upon activity being detected |
|
High Performance • High performing data communication to/from the highly distributed Edge environment • Edge equipment fully supported without requiring customization • High availability, no single point of failure
|
• Solution architecture developed to collect, process and log massive amounts of data, at scale, without a performance impact across entire Edge infrastructure • Continuous processing of all asset location data providing immediate awareness and tracking of movement activity • Continuous processing of all key environmental conditions providing immediate awareness of the impact and root-cause of issues • Integration with service management solutions ensuring support service levels are met |
|
Remote Control • Remote control and monitoring of IT assets and environmental systems • Environmental conditions monitored with alerts created when exceptions are detected • Asset movement and access to facility monitored and tracked
|
• Motion detection, asset movement, physical asset access, environment change are examples of how CenterScape provides control to all Edge and data center locations • Low/no touch technology delivering a holistic view of the Edge infrastructure environment and computer equipment even when there’s an impact on the remote locations power and network. |
|
Secure • Connectivity to and within Edge secured in-line with industry and corporate policy • Edge management tools provide and enforce access permissions for different roles • Real-world view of physical access and subsequent activity at all Edge locations
|
• The single, trusted source, to monitor access at Edge locations, recording activities and providing video and alerts when racks are opened and/or assets are moved • Scheduled maintenance activity monitored and guided remotely
|
|
End User / Consumer Focused • Consumer experience captured and used to measure Edge success • Edge managed and supported in-line with the business service levels • Continual location comparisons enable efficiency and performance change and identify and eliminate issues and weaknesses
|
• Environmental tracked to show variations from normal conditions high-lighting potential business impacting issues • Edge locations monitored holistically with data that allow comparisons to be made between poor and well performing locations • Environmental issue impacts managed in line with business severity • Environmental conditions mapped directly with the business assets effected allowing business impact to be assessed and remediated in-line with SLA’s |
|
Heterogeneous • Edge managed consistently irrespective of technology type or vendor • Out-of-the-box management support for all Edge systems • Elimination/abstraction of proprietary hardware monitoring
|
• Provides an abstraction layer, monitoring, collecting and processing environmental power and cooling data, irrespective of what equipment is used. • Zero-impact, zero-cost monitoring when new environmental equipment is introduced • Eliminates the silos that are created when monitoring equipment by type or vendor • All assets tracked agnostically, no customization, no network • Integration with all leading Service Mgmt. and DCIM products providing a comprehensive view of the Edge infrastructure while ensuring SLA’s are met |
|
High Scale • Management scales to hundreds or thousands of different size locations • Locations added and removed without impacting business • Performance delivered consistently across all locations
|
• Edge environment monitored and viewed holistically and at massive scale • Solution architecture developed to manage highly diverse, highly dispersed, environments and assets providing the on-going collection, unification and processing of collected data • Used by customers to monitor and track the movement of over a million assets |
The Edge Common Attributes are table-stakes. A product that does not exhibit the Edge Common Attributes is not an Edge product. In Part 2 of this series we take a look at the Edge attributes that differentiate products.
Are you developing an edge data center deployment strategy? Preparation is the key to success. Download our free white paper "Standing at the Edge? Look Before You Leap," and understand the advantages — and the risks — of Edge deployments.